
Conservation Incentive Contracts are an option available through EQIP that offers producers financial assistance to adopt conservation management practices on working landscapes.
About EQIP Conservation Incentive Contracts
NRCS provides technical and financial assistance to producers through Environmental Quality Incentive Program Conservation Incentive Contracts (EQIP-CIC) for the implementation, adoption, management, and maintenance of incentive practices that effectively address at least one eligible priority resource concern within the State-identified high priority area (HPA). Producers may use incentive contracts as a “steppingstone” from correcting resource issues on specific land units through EQIP, to achieving sustainable stewardship on their entire operation.
Details
- Requires producers to address at least one priority resource concern during the contract period.
- Has an initial length of five years.
- Has a payment limitation of $200,000 for the life of the 2018 Farm Bill.
- Offers two types of payments:
- Implementation payments, which are paid after certification of the conservation practice.
- Annual payments, which include management practices, paid as soon as practicable, after October 1 of each fiscal year.
- Offers higher payment rates and advance payments to historically underserved (HU) producers who implement conservation practices in an EQIP Conservation Incentive Contract.
Montana High Priority Areas
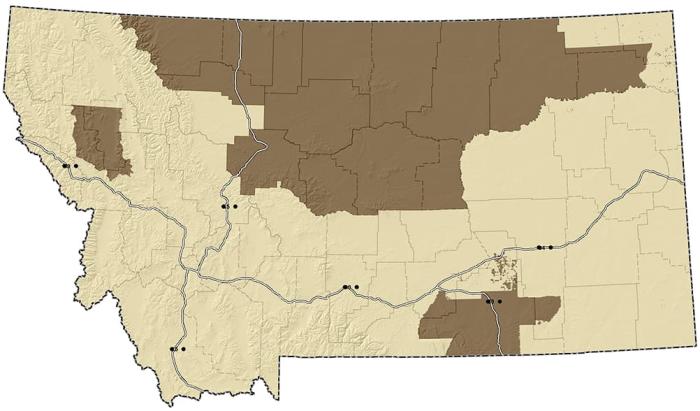
CIC High Priority Area 1 in Montana includes the Blackfeet, Crow, Flathead, Fort Belknap, Fort Peck, Northern Cheyenne, and Rocky Boys Reservations as well as Glacier, Toole, Liberty, Hill, Blaine, Phillips, Petroleum, Fergus, Judith Basin, Cascade, Chouteau, and Pondera Counties and parts of Treasure and Big Horn Counties.
Priority Resource Concern Categories
- Degraded Plat Condition
- Livestock Production Limitations
- Soil Quality Limitations
Eligible Land Uses
Eligible land uses are cropland, forest, range, pasture, farmstead and associated land. EQIP assistance can be used on many types of operations, including, but not limited to:
- Conventional and organic or transitioning to organic
- Specialty crops and commodity crops
- Forestry and wildlife
- Livestock operations
Eligible Conservation Practices
- 101 CNMP Design and Implementation Activity
- 102 Comprehensive Nutrient Management Plan
- 106 Forest Management Plan
- 110 Grazing Management Plan
- 116 Soil Health Management Plan
- 120 Agricultural Energy Design
- 138 Conservation Plan Supporting Organic Transition
- 140 Organic Transition Design and Implementation Activity
- 144 Fish and Wildlife Habitat Design and Implementation Activity
- 148 Pollinator Habitat Design and Implementation Activity
- 157 Nutrient Management Design and Implementation Activity
- 158 Feed Management Design and Implementation Activity
- 159 Grazing Management Design and Implementation Activity
- 160 Prescribed Burning Design and Implementation Activity
- 161 Pest Management Conservation System Design and Implementation Activity
- 162 Soil Health Design and Implementation Activity
- 163 Irrigation Water Management Design and Implementation Activity
- 164 Improved Management of Drainage Water Design
- 165 Forest Management Design and Implementation Activity
- 199 Conservation Plan
- 204 Adaptive Management for Soil Health
- 206 Feed and Forage Analysis
- 207 Soil Assessment and Soil Testing for Contaminants Activity
- 209 PFAS Testing in Water or Soil
- 216 Soil Health Testing
- 217 Soil and Source Testing for Nutrient Management
- 218 Carbon Sequestration and Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Assessment
- 219 Prescribed Grazing Conservation Evaluation and Monitoring Activity
- 221 Soil Organic Carbon Stock Monitoring
- 222 Indigenous Stewardship Methods Evaluation
- 223 Forest Management Assessment
- 224 Aquifer Flow Test
- 226 Waste Facility Site Suitability and Feasibility Assessment
- 227 Evaluation of Existing Waste Storage Facility Components
- 228 Agricultural Energy Assessment Activity
- 328 Conservation Crop Rotation
- 329 Residue and Tillage Management, No-Till
- 336 Soil Carbon Amendment
- 338 Prescribed Burning
- 340 Cover Crop
- 345 Residue and Tillage Management, Reduced Till
- 368 Emergency Animal Mortality Management
- 449 Irrigation Water Management
- 484 Mulching
- 511 Forage Harvest Management
- 528 Prescribed Grazing
- 548 Grazing Land Mechanical Treatment
- 554 Drainage Water Management
- 590 Nutrient Management
- 595 Integrated Pest Management
- 610 Salinity and Sodic Soil Management
- 644 Wetland Wildlife Habitat Management
- 645 Upland Wildlife Habitat Management
- 647 Early Successional Habitat Development/Management
At least one management practice must be included in the application to be eligible for EQIP-CIC.
When to Apply
Program applications are accepted on a continual basis. However, NRCS establishes application ranking dates for evaluation, ranking and approval of eligible applications. Applications received after the ranking date will be automatically deferred to the next funding period. See Montana Programs and Application Dates.
Applications must meet the intent of this initiative. For more details about this initiative, contact your local field office.
Local Ranking Questions
NRCS uses these questions to evaluate eligible applications for this project and to prioritize applications for potential funding.
Which of the following individual Priority Resource Concern Categories will be addressed with this application? (Select all that apply)
- Degraded Plant Condition
- Livestock Production Limitation
- Soil Quality Limitations
- None of the above
How many management practices will be applied with this application? (Select only one)
- One
- Two
- Three
- 4 or more management practices
- No management practices
Will the applicant implement any management practice for multiple years during the 5-year contract period? (Select only one)
- All 5 years of the contract
- 3 to 4 years of the contract
- Less than 3 years of the contract
- None of the above
Additional Montana Information
Additional Information
Apply for Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP)
The Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) provides financial and technical assistance to agricultural producers and non-industrial forest managers.
Learn MoreFarm Bill
The 2018 Farm Bill was enacted on December 20, 2018. The Farm Bill continues its strong support for conservation efforts of America’s farmers and ranchers through reauthorization and expanded flexibility of NRCS conservation programs.
Learn MoreReady to get started?
Contact your local service center to start your application.
How to Get Assistance
Do you farm or ranch and want to make improvements to the land that you own or lease?
Natural Resources Conservation Service offers technical and financial assistance to help farmers, ranchers and forest landowners.

To get started with NRCS, we recommend you stop by your local NRCS field office. We’ll discuss your vision for your land.
NRCS provides landowners with free technical assistance, or advice, for their land. Common technical assistance includes: resource assessment, practice design and resource monitoring. Your conservation planner will help you determine if financial assistance is right for you.
We’ll walk you through the application process. To get started on applying for financial assistance, we’ll work with you:
- To fill out an AD 1026, which ensures a conservation plan is in place before lands with highly erodible soils are farmed. It also ensures that identified wetland areas are protected.
- To meet other eligibility certifications.
Once complete, we’ll work with you on the application, or CPA 1200.
Applications for most programs are accepted on a continuous basis, but they’re considered for funding in different ranking periods. Be sure to ask your local NRCS district conservationist about the deadline for the ranking period to ensure you turn in your application in time.
As part of the application process, we’ll check to see if you are eligible. To do this, you’ll need to bring:
- An official tax ID (Social Security number or an employer ID)
- A property deed or lease agreement to show you have control of the property; and
- A farm number.
If you don’t have a farm number, you can get one from USDA’s Farm Service Agency. Typically, the local FSA office is located in the same building as the local NRCS office. You only need a farm number if you’re interested in financial assistance.
NRCS will take a look at the applications and rank them according to local resource concerns, the amount of conservation benefits the work will provide and the needs of applicants. View Application Ranking Dates by State.
If you’re selected, you can choose whether to sign the contract for the work to be done.
Once you sign the contract, you’ll be provided standards and specifications for completing the practice or practices, and then you will have a specified amount of time to implement. Once the work is implemented and inspected, you’ll be paid the rate of compensation for the work if it meets NRCS standards and specifications.

