
NRCS uses Landscape Conservation Initiatives to accelerate the benefits of voluntary conservation programs, such as cleaner water and air, healthier soil and enhanced wildlife habitat.
Landscape and conservation initiatives enable NRCS to more effectively address priority natural resource concerns by delivering systems of practices, primarily to the most vulnerable lands within geographic focus areas.
Through targeted funds, cooperation with partners and locally led efforts, NRCS is able to utilize landscape initiatives to address landscape-scale natural resource concerns, such as species conservation and water quality, that transcend farm, county, and state boundaries.
Conservation initiatives create specialty funding pools to help famers implement priority conservation practices on their land address resource concerns related to soil, water and air quality, energy consumption, and wildlife habitat.
Landscape Initiatives in Indiana

Great Lakes Restoration Initiative
GLRI funding is added to the regular funding NRCS receives each year for its Farm Bill conservation programs in order to accelerate Great Lakes protection and restoration. Through Farm Bill conservation programs, NRCS provides technical and financial assistance to landowners, enabling them to make conservation improvements to their land. This assistance helps them plan and implement a variety of conservation practices, such as planting cover crops, adopting no-till, removing invasive plants and restoring wetlands.
GLRI funds are targeted to priority watersheds to implement avoiding, controlling and trapping practices (e.g. nutrient management, drainage water management, cover crops, waste storage facilities, cover crops and residue) that reduce the amount of nutrient loss from agricultural lands.
Indiana GLRI Priority Watersheds include:
* Auglaize
* St. Marys
* St. Joseph - Maumee
* Upper Maumee

Mississippi River Basin Healthy Watershed Initiative
Launched in 2009, the 12-state Mississippi River Basin Healthy Watersheds Initiative (MRBI) uses several Farm Bill programs, including the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) and the Agricultural Conservation Easement Program (ACEP), to help landowners sustain America’s natural resources through voluntary conservation. The overall goals of MRBI are to improve water quality, restore wetlands and enhance wildlife habitat while ensuring economic viability of agricultural lands.
The initiative has helped increase the adoption of critical water quality conservation practices, such as cover crops, no-till, residue management, grassed waterways and nutrient management,
Indiana MRBI Priority Watersheds include:
- Lower Salt Creek (Implementation Phase)
- Sugar Creek Shelby County SWCD (Planning Phase)
- Headwaters Four Mile (Planning Phase)
- Buckhorn Creek

National Water Quality Incentive
Now in its eleventh year, the National Water Quality Initiative is a partnership among NRCS, state water quality agencies and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to identify and address impaired water bodies through voluntary conservation. NRCS provides targeted funding for financial and technical assistance in small watersheds most in need and where farmers can use conservation practices to make a difference.
Conservation systems include practices that promote soil health, reduce erosion and lessen nutrient runoff, such as filter strips, cover crops, reduced tillage and manure management. These practices not only benefit natural resources but enhance agricultural productivity and profitability by improving soil health and optimizing the use of agricultural inputs.
Indiana NWQI watersheds include:
- Lake Wawasee (Implementation Phase)
- Muncie Creek White River (Implementation Phase)
- Upper Blue Sinking (Implementation Phase)
- Eagle Creek (Monitoring Phase)
- Clear Lake (Planning Phase)

Source Water Protection
Source water refers to sources of water (such as rivers, streams, lakes, reservoirs, springs and groundwater) that provide water to public drinking water supplies and private wells. Source water protection includes a wide variety of actions and activities aimed at safeguarding, maintaining or improving the quality and/or quantity of sources of drinking water and their contributing areas.
The 2018 Farm Bill added a provision providing for the protection of source water through targeted conservation practices. See the map below for the high priority areas in Indiana targeted for water quality improvements:


Western Lake Erie Basin Initiative
The United States and Canada have formed a partnership to prioritize the restoration of Lake Erie and the other Great Lakes. As part of that effort, the USDA's Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), along with five other federal agencies, state and other non-government, industry and academic partners, are dedicated to accelerating Lake Erie’s rehabilitation by reducing phosphorus loading through a number of collaborative projects and initiatives. By providing technical and financial assistance to farmers to implement conservation practices, NRCS can assist in the comprehensive effort to improve water quality, soil health and sustain the region’s economic viability.
The West Lake Erie Basin (WLEB) Initiative aims to protect and preserve the water resources of the Western Lake Erie Basin. By initiating a cooperative watershed planning process, both short and long-term water conservation needs in the basin can be met. Numerous Farm Bill programs as well as other Federal, State, local and nonprofit programs are available to assist basin landowners to adopt these conservation practices.
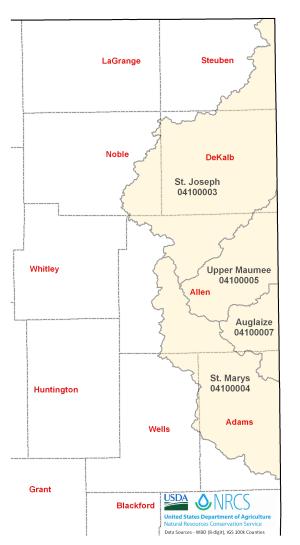
Indiana WLEB watersheds include:
- St Joseph
- Upper Maumee
- Auglaize
- St. Mary's
Conservation Initiatives in Indiana

CSP Grasslands Conservation Initiative
CSP-GCI is a new program authorized by the 2018 Farm Bill.
This new initiative assists producers in protecting grazing land uses; conserving and improving soil, water and wildlife resources; and achieving related conservation values by conserving eligible land through grassland conservation contracts. Eligible lands are limited to cropland for which base acres have been maintained under FSA’s ARC/PLC and were planted to grass or pasture, including idle or fallow, during a specific period. Enrolled acreage must be managed consistently with a grassland conservation plan. Producers will have a single opportunity to enroll eligible land in a five-year contract.

High Tunnel Initiative
Partnership Opportunities

Conservation Innovation Grants (CIG)
Conservation Innovation Grants (CIG) is a competitive program that supports the development of new tools, approaches, practices, and technologies to further natural resource conservation on private lands. Through creative problem solving and innovation, CIG partners work to address our nation's water quality, air quality, soil health and wildlife habitat challenges, all while improving agricultural operations.
Indiana does not offer state specific CIG opportunities but national opportunities are available.

