Evaluation of Watershed Models
Evaluation of Watershed Models
Project Name: Evaluation of Watershed Models to Simulate Conservation Practices in Jobos Bay Watershed, Puerto Rico
NRCS Project Members: Candiss O. Williams, Candiss.Williams@lin.usda.gov
Cooperators: Richard Lowrance, Lowrance.Richard@epa.gov; Timothy Strickland, tim.strickland@ars.usda.gov; David Bosch, david.bosch@ars.usda.gov; Thomas Potter, retired; Randall Williams, randy.williams@ars.usda.gov; Jimmy Williams, jwilliams@brc.tamus.edu; Evelyn Steglich, esteglich@brc.tamus.edu
Relevance
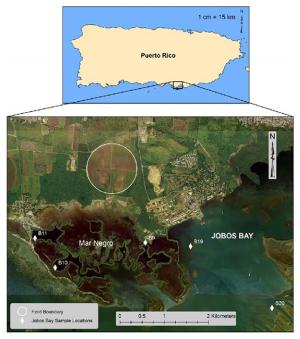
Map showing Jobos Bay sample locations.
The project originated from an ongoing collaboration between USDA (U.S. Department of Agriculture) and NOAA on the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. The Conservation Effects Assessment Project (CEAP) was developed in 2003 by the USDA as a multi-agency effort to quantify the environmental benefits of conservation practices applied by private landowners. Ten Special Emphasis Watersheds (SEW) were identified throughout the U.S. to address specific resource concerns such as animal feeding operations, water use, drainage management and wildlife habitat restoration. The Jobos Bay watershed was selected by CEAP partners as the first tropical CEAP SEW with the goal of identifying innovative conservation practices that will enhance the health of coral reef ecosystems. The project’s general approach includes describing the baseline conditions in Jobos Bay, implementing agricultural conservation practices on the watershed and measuring the response in Jobos Bay’s water quality, biogeochemistry, benthic habitats and marine biota. It is anticipated that relatively short term changes will be measured in water quality and marine sediments; while long-term changes in higher trophic levels, such as fishes, may be detected in out-years.
Objective
Evaluate suitable field and watershed models to simulate hydrologic events occurring in Jobos Bay and use calibrated models to predict potential delivery of water, sediment, and nutrients to the Bay.
Approach
Conducted field-level studies on a silage farm adjacent to JBNERR, including groundwater and surface water monitoring of nutrients and pesticides, assessment of current BMPs and water quality modeling. Data from the field studies were used to develop the databases for the Agricultural Policy Environmental eXtender (APEX) and Riparian Ecosystem Management Model (REMM) models. In this study, we simulated the water quality and hydrology of a portion of the Jobos Bay watershed, Puerto Rico using two models, one for simulating the upland agricultural field and one for simulating the adjacent riparian zone. The model used to simulate upland field outputs was the Agricultural Policy/Environmental eXtender (APEX) model and the model used to simulate riparian functions was the Riparian Ecosystem Management Model (REMM).
Outputs and Products
Conservation recommendations were provided in the local area. Work by USDA ARS and NOAA is ongoing.
Williams, C.O., R. Lowrance, T.L. Potter, D. D. Bosch, R. Hubbard, T. Strickland, R. G. Williams, J.R. Williams, A. Dieppa, and D. Sotomayor. 2016. APEX and REMM simulation of atrazine transport within a coastal zone in Southeastern Puerto Rico. Journal of Environmental Modeling & Assessment. DOI: 10.1007/s10666-016-9508-4.
Williams, C.O., Lowrance, R.R., Bosch, D.D., Williams, J.R., Dieppa, A., Hubbard, R.K., Mas, E., Sotomayor, D., Potter, T.L., Steglich, E.M., Strickland, T.C., Williams, R.G. 2013. Hydrology and water quality of a field and riparian buffer adjacent to a mangrove wetland in Jobos Bay Watershed, Puerto Rico. Ecological Engineering. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.09.005 offsite link image .
Lowrance, R., C. Williams, A. Tilak, M. Burchell, R. Williams 2012. Applications of the Riparian Ecosystem Management Model (REMM) (Oral Presentation). American Water Resources Association Summer Specialty Summer Conference on Riparian Ecosystems, Denver, Colorado.
Williams, C.O., T. Potter, and R. Lowrance. 2013. APEX sensitivity to atrazine dissipation rate on surface runoff loss within a coastal zone in Southeastern Puerto Rico (Oral Presentation). American Chemical Society, Indianapolis, Indiana.
Williams, C.O. R. Lowrance, and R. Williams. 2013. Evaluation of APEX and REMM Models to Simulate Water Quality Benefits of Riparian Buffers in the Jobos Bay Watershed (Oral Presentation). American Water Resources Association Spring Specialty Conference on Agricultural Hydrology and Water Quality II, St. Louis, Missouri.
Williams, C.O. R. Lowrance, and R. Williams. 2012. Application of APEX and REMM in Evaluating Water Quality Benefits of Riparian Buffers (Oral Presentation) in Symposium-Modeling Hydrologic Processes in Soils and Landscapes. Soil Science Society of America Annual Meeting, Cincinnati, Ohio.
Williams, C.O., R. Lowrance, R. Williams, J. Williams, A. Dieppa, D. Sotomayor, E. Mas, T. Strickland, D. Bosch, R. Hubbard, and T. Potter. 2011. A Combined Modeling Approach to Evaluate Water Quality Benefits of Riparian Buffers in the Jobos Bay Watershed. American Society of Limnology and Oceanography Annual Meeting, San Juan, Puerto Rico.

